I hear about Metaverse all the time but the definition can be slightly different based on whom I ask. In a pre-MWC webinar on Open RAN, I was even asked "What exactly is Metaverse and would it work on Open RAN?" 😁
I found this explanation from Bloomberg the simplest way to explain Metaverse:
The metaverse is a virtual universe that blends aspects of digital technologies including video-conferencing, games like Minecraft or Roblox, cryptocurrencies, email, virtual reality, social media and live-streaming. Quite how these pieces will fit together is a work in progress, but some tech giants already see it as the future of human communication and interaction. It’s “the next frontier,” Mark Zuckerberg said when he changed his company’s name from Facebook to Meta Platforms Inc. Commercial opportunities in the metaverse are one reason why Microsoft Corp. is buying game publisher Activision Blizzard Inc. in its biggest ever deal.
A recently published paper on arXiv explains it as:
The metaverse is not a new idea because it has circulated along with the development of the Internet and other technologies for decades. Fig. 2 above describes the timeline of the metaverse development that involves many primary events, from the birth of the Internet and the first mention in literature to the first virtual world project with Second Life and recent metaverse projects of big tech companies like Microsoft and Facebook. Metaverse is the term formed by combining Meta and Universe, which may be first mentioned in the dystopian cyberpunk novel Snow Crash in 1992 to describe a virtual reality world called the matrix. At present, the metaverse is defined as a shared virtual 3D world or even multiple cross-platform worlds that can provide users a comprehensively immersive experience with interactive and collaborative activities. Besides virtual places and constructions fixed in the virtual world, many other entities, such as objects, user identities, and digital goods, can be exchanged between different virtual worlds and even reflected into the reality world.
In their blog post, Ericsson explains:
The concept of metaverse does not belong to Meta, of course. It thus means different things depending on who you ask. We could share formal definitions here, but would rather concentrate on the three important elements each of these definitions embrace.
First, and most importantly, the metaverse embraces a social element. It is not only a virtual space where users spend time (and money) on their own or with a selected few. Rather, the metaverse is intended to resonate with the very social fabric which underpins human society. Once in the metaverse, you and/or your avatar are able to interact humanly by looking into each other’s eyes, perceive body language and maybe even shake hands or hug each other.
Second, it has a strong virtual narrative. For some, the metaverse exists in a purely virtual world which can be consumed by us through VR headsets; an example here is the game Fortnite played with metaverse VR interaction using such headsets. For others, it has a strong foundation in the physical world but with digital overlays experienced through augmented reality (AR) or the more interactive mixed reality (MR). An example here is Pokémon Go played through a mobile phone or AR glasses. Either way, our experiences and ways of social interaction are significantly augmented with persistent virtual content. Access to the virtual world of the metaverse and haptic interaction therein is enabled by any of these 3D eXtended Reality (XR) devices, and in the interim via today’s 2D screens leveraging WebXR technologies.
Third, it is accelerated through novel technologies, like Web 3.0, blockchains, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), 5G, digital twins, artificial intelligence and XR devices, just to name a few. It is important to understand that the metaverse could probably exist without most of these tech ingredients, but uptake and scale would be seriously hampered. We will give a few examples further down, once we have discussed the building blocks of the metaverse in more detail.
Going back to the arXiv paper:
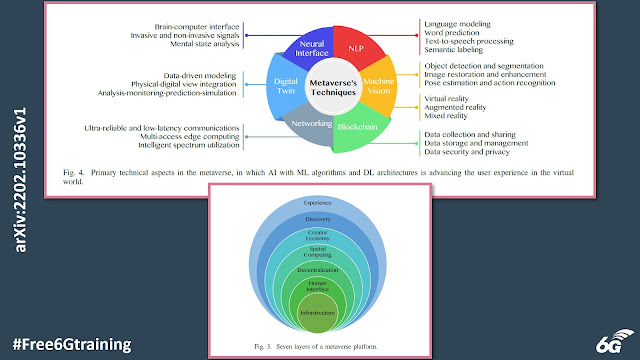
A metaverse platform can include several layers (see Fig. 3) which are expressed as follows:
- Infrastructure: 5G, 6G, WiFi, cloud, data center, central processing units, and GPUs.
- Human interface: mobile, smartwatch, smartglasses, wearable devices, head-mounted display, gestures, voice, and electrode bundle.
- Decentralization: edge computing, AI agents, blockchain, and microservices.
- Spatial computing: 3D engines, VR, augmented reality (AR), XR, geospatial mapping, and multitasking.
- Creator economy: design tools, asset markets, Ecommerce, and workflow.
- Discovery: advertising networks, virtual stores, social curation, ratings, avatar, and chatbot.
- Experience: games, social, E-sports, shopping, festivals, events, learning, and working.
It is not hard to find out the presence of AI inside layers, with machine learning (ML) algorithms and deep learning (DL) architectures, along with their importance in many diversified aspects.
By merging AI with other technologies, such as AR/VR, blockchain, and networking, the metaverse can create secure, scalable, and realistic virtual worlds on a reliable and alwayson platform. According to the seven-layer metaverse platform, it is undoubted to realize the important role of AI to guarantee the reliability of infrastructure and improve its performance so far. In the 5G and future 6G systems, many advanced ML algorithms with supervised learning and reinforcement learning have been adopted for different challenging tasks, such as efficient spectrum monitoring, automatic resource allocation, channel estimation, traffic off-loading, attack prevention, and network fault detection. With sensor-based wearable devices and other human-machine interaction gadgets, simple human movements and complex actions can be analyzed and recognized based on learning ML and DL models. Therefore, users’ movements in the real world are projected into the virtual worlds, allowing users to fully control their avatars to interact with other objects in the metaverse comfortably. Moreover, these avatars can engage with many modalities adopted in the real world, such as facial expressions, emotions, body movement, and physical interactions, besides speech recognition and sentiment analysis, which are powered by AI in terms of accuracy and processing speed.
The paper goes on to investigate the state-of-the-art AI-based methods in six technical aspects: natural language processing, machine vision, blockchain, networking, DTs, and neural interface; which present the potential for the metaverse as shown in Fig. 4. Accordingly, the experience of users in the metaverse is enhanced significantly with nearly no boundary between the virtual world and the real world. You can read the complete paper here.
Metaverse is also a target of lots of jokes at the moment. One such example is in the Tweet below.
Who did this!😂😂😂 pic.twitter.com/P9tZC5XqnG
— Subrahmanyam KVJ (@SuB8u) July 29, 2021
Finally, here is a short presentation within a longer video by Michael Patent, Founder & President, Culture Group that is embedded below. I am starting at 4 mins 49 seconds but if you want to listen to entire talk, just start from the beginning:
Related Posts:
- Free 6G Training: What is Extended Reality (XR)?
- Free 6G Training: Three Degrees of Freedom (3DoF) vs Six (6DoF) in Extended Reality
- Free 6G Training: One XR Device to Rule Them All!
- Free 6G Training: Brain-to-Text Communication via Handwriting
- Free 6G Training: Brain Computer Interface (BCI) and Internet of Senses (IoS)
- Free 6G Training: NGMN Releases 6G Use Cases and Analysis White Paper
- 3G4G: Free 'An Introduction to 6G' Training Course Online
- 3G4G: 6G and Beyond-5G Wireless Technology



Comments
Post a Comment