We have talked about Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS), also known as Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) in many different posts. The other commonly used term for them is Metasurface. When we generally talk about IRS/RIS, we are talking about active or passive reflective metasurfaces. The Transmissive Metasurface is also referred to as Metasurface lens as it allows the signal to go through but can be guided to a point of interest.
This week, Kyocera Corporation announced that they have developed a Transmissive Metasurface technology that can redirect wireless network signals in a specific direction to improve the coverage area and performance of 5G and eventually 6G networks. The official announcement says:
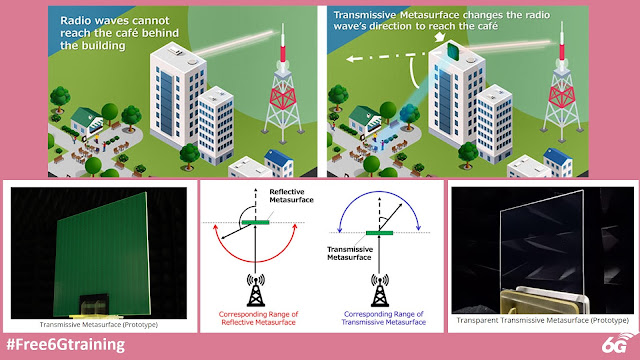
Kyocera Develops Transmissive Metasurface Technology for B5G and 6G. The Transmissive Metasurface will help deliver high-frequency millimeter-wave 5G and 6G to places where communication is impossible due to obstacles, expanding service areas beyond the capability of conventional Reflective Metasurface technologies used today.
The 28 GHz band used in 5G networks, and the higher frequency band being studied for 6G, have a high degree of rectilinear propagation. Signals often cannot reach locations where a direct line of sight to the base station is obstructed. Reflective Metasurface technology offers a very limited ability to change the direction of a signal to reach these areas. To solve this issue and expand performance, Kyocera developed a new Transmissive Metasurface technology that can redirect radio waves at smaller angles to extend targeted network coverage.
Features: Transmissive Metasurface Technology
1) Kyocera expands the direction in which radio signals can be redirected: Radio waves striking a conventional Reflective Metasurface device can be redirected at a wide angle, but not at narrow angles beyond the metasurface. Kyocera's new Transmissive Metasurface technology is able to bend at narrow angles in order to avoid obstacles that may block transmission, expanding 5G and eventually 6G coverage even further. For example, a large building may block 5G network transmission, but Kyocera's Transmissive Metasurface device can redirect the signal downward to reach smaller buildings behind and below for better coverage.
2) Proprietary Flexible Size Development: The area in which a Transmissive Metasurface can deliver signals is proportional to the size of the metasurface itself. Conventional technologies have been unable to develop a Transmissive Metasurface of sufficient size for practical use, but Kyocera can design any size using its proprietary technology, allowing greater flexibility. This makes it possible to install metasurfaces in more places, such as a home patio or apartment balcony.
Kyocera is developing a Transparent Transmissive Metasurface that is more landscape-friendly and incorporates technological improvements to focus radio waves in specific locations and improve signal strength further. Additionally, the Company is developing a Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) that can create a smart signal environment to change the signal direction adaptively depending on the devices in use.
The video below (in Japanese), explains their transmissive metasurface:
As this technology develops further, it would be interesting to see if a generic metasurface lens could be created for a wide range of frequencies, rather than a single one. Also, could the frequency be modified while the metasurface is in operation. Surely some researchers are already working on these.
Related Posts:
- Free 6G Training: Communications Using Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces in B5G & 6G
- Free 6G Training: Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS) for Wireless Communications
- Free 6G Training: Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) Use Cases
- Free 6G Training: ZTE Showcases Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) Prototypes at MWC 2022
- Free 6G Training: NTT Docomo presents HAPS, Metasurface lens and Pinching antenna at MWC 2021
- Free 6G Training: Smart Radio Environments Empowered by Reconfigurable AI Meta-Surfaces
- Free 6G Training: '6G Vision for 2030+' from 6th Generation Innovation Centre (6GIC)
- Free 6G Training: Special Articles on 5G Evolution & 6G in NTT Docomo Technical Journal
- Free 6G Training: Softbank's 12 Challenges for Beyond 5G / 6G
- Connectivity Technology Blog: Docomo and AGC use Metasurface Lens to Guide Millimeter Waves (mmWaves) Indoors
- Connectivity Technology Blog: Futuristic Glass Antenna by NTT Docomo and AGC
- 3G4G: 6G Technologies - Introduction from 6G Training
- 3G4G: Free 'An Introduction to 6G' Training Course Online
- 3G4G: 6G and Beyond-5G Wireless Technology

Comments
Post a Comment